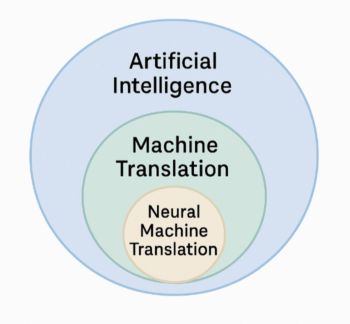
Artificial Intelligence Translation (AIT) – the big umbrella
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science focused on making computers and machines “smart”— making them capable of learning, reasoning, and solving problems like humans.
- Artificial Intelligence Translation (AIT) is any translation done using artificial intelligence — this includes older rule-based systems, statistical models, and newer neural approaches.
- The techniques used could be one of:
- Rule-Based Machine Translation (RBMT): which uses grammar rules and dictionaries.
- Statistical Machine Translation (SMT): which is based on probabilities and aligned text corpora.
- Neural Machine Translation (NMT): which uses modern deep learning–based models.
- AIT is a general category which includes NMT and older, less advanced methods.
Machine Translation (MT) — a subfield of AIT
- Machine Translation (MT) is any technology that automatically translates text or speech from one language to another language using computational methods.
- The techniques used include:
- Rule-Based MT (RBMT)
- Statistical MT (SMT)
- Neural MT (NMT) Goal: Break language barriers using algorithms.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) — a subfield of MT
- Neural Machine Translation (NMT) is the most advanced form of machine translation using deep learning and neural networks.
- It is a specific type of AI translation which uses neural networks, especially deep learning, to translate text in a more fluent, context-aware way.
- It was introduced between 2014 and 2016, and quickly replaced SMT on the top internet platforms (such as Google Translate, Microsoft Translator and DeepL).
- Strengths:
- It handles long-range context better.
- provides more natural and fluid translations,
- is better at idioms and complex grammar.
- Advantages:
- Understands context better.
- More fluent and natural translations.
- Learns from massive datasets (i.e., millions of translated sentences).
What are Neural Networks
A neural network is a computer program designed to work like the human brain. It learns by adjusting connections between artificial “neurons” based on examples (data). It is inspired by how a human brain has billions of neurons connected by synapses.
- Made of:
- Input Layer: takes in data (like pixels of an image or words in a sentence).
- Hidden Layers: processes and transforms the information through math and weighting processes.
- Output Layer: produces a result (like recognizing a cat in a photo or translating a sentence).
- Learning:
- Neural networks improve themselves over time by making guesses, checking if they’re wrong, and adjusting their internal connections to do better next time — a process called “training”.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning It is a type of machine learning in which computers use very large, complex neural networks to learn from very large amounts of data.
Deep learning = Neural networks with many layers, designed to handle really complicated tasks by learning from vast amounts of data.
- “Deep” means that it has many hidden layers between input and output — not just one or two, but possibly dozens or even thousands!
- More layers means that the network can learn more complex patterns.
Why use deep learning? Because simple models can’t handle complicated stuff like:
- Understanding natural language (like translation or conversation).
- Recognizing objects in photos.
- Playing video games at a superhuman level.
Examples:
- ChatGPT (understanding language).
- Self-driving cars (seeing and reacting to the road).
- Netflix recommendations (predicting what you’ll like).
Quick Relationship:
| Term | What it means |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Teaching computers to learn from data. |
| Neural Networks | A method within machine learning that mimics the brain. |
| Deep Learning | Neural networks, but much bigger and deeper! |
AZ World Translation has used Neural Machine Translation for several years as a tool in our translation process for improved speed and efficiency..
If you need to bridge the language divide and connect with a broader audience, contact us at info@a-zworld.ca or visit www.a-zworld.ca the AZ World team will be happy to assist you.

